
Then, using the command mentioned below, list all the permissions for these files: In the first place, let’s make a directory (test) with files named as “test1.txt” and “test2.txt”: To find more info on chown command, you can use this command mentioned below:

#Chmod 777 recursively trial#
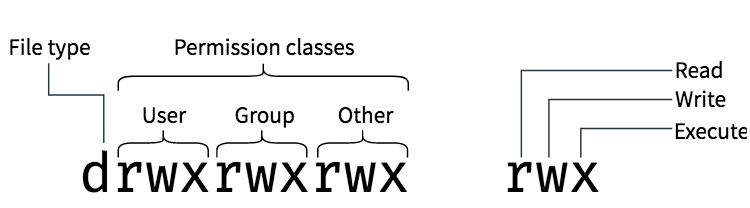
Start your 30-day free trial to get your hands on in-demand CompTIA certifications. Here the USER is the client, and GROUP is the group name, of course, and FILES is the file/files in the directory. The chown command’s syntax is as follows: Others – Users who are not the owner nor an individual from the group. Group – All clients have a primary group and they own the file, which is helpful for sharing files or giving access. Owner – Process or person who made the file. Sysadmins can implement a security strategy dependent on file authorizations. You can utilize file permissions to control access to their files. Exploring File Permissions with Chmod and Chown Command The chmod command, likewise known as change mode, is utilized to change/alter permissions of a given file as indicated by a specific mode. The chown means "change owner" and is utilized to change/alter the owner of a given file or directories. The chown and chmod are popular command-line commands that are utilized to tackle access management of different files in Linux-based OS computers.

Start your 30-day free trial to gain access to over 900 self-paced courses. Chmod and chown are the tools we use to control possession and access permissions of files and directories. Just as the subtleties of proprietorship, each file has metadata about its access permissions. Likewise, two clients and groups can be the proprietors of files and registries. In Linux, clients can have a place with at least one group. The commands utilized in this blog post should work in other POSIX- compliant shells also. In this short instructional blog post, we will examine two tools for empowering clients to access files: chmod and chown. It has a security system set up that controls which clients and groups approach the files and indexes in the system. The Linux operating system is a multi-user operating system.
#Chmod 777 recursively software#
Offered With The Following Universities:.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
